Health
COVID-19: Nigeria yet to meet 70% vaccination target — FG
The Federal Government says the country has only vaccinated 68 per cent of it’s COVID-19 eligible population.
The government in 2021, said it had invested much and was ready to vaccinate 70 per cent of its population before the end of 2022.
But as of Feb. 7, the country had only vaccinated 68 per cent of the COVID-19 eligible population.
Dr Faisal Shuaib, Executive Director, National Primary Health Care Development Agency, (NPHCDA), said this on Thursday in Abuja.
He spoke at the First Quarter Review Meeting of the Northern Traditional Leaders Committee on PHC Delivery (NTLC).
Similarly, Mr Boss Mustapha, Secretary to the Government of the Federation and also Chairman, PSC on COVID-19, had also in December 2021, said the country invested in enough vaccines to cover over 70 per cent of the country’s eligible population.
Mustapha said the vaccines were safe and efficacious, hence it was better and safer to be vaccinated against the virus.
In spite of that, Shuaib, at the current review meeting, commended the NTLC for their support for Primary Health Care services.
He reiterated that the fight against COVID-19 was not over until the country attained 70 per cent target coverage of vaccination.
He further said the country needed to look beyond reducing the numbers of circulating Vaccine Derived Polio Virus type 2 (cVDPV2) by over 90 per cent, to get down to zero, adding that the target for 2023 was not just reduction, but getting it to zero.
The NPHCDA further noted that to eradicate all forms of disease outbreaks, states and LGAs Community Leaders should improve their routine immunization.
The Minister of Health, Dr Osagie Ehanire, while appreciating the role of NTLC, said the gains that were made over the years in PHC service delivery, were largely attributed to the role of traditional leaders.
Ehanire said that routine immunisation was a standard service of PHCs and was free, safe, effective and available across the country.
“Parents and caregivers need to be mobilised to ensure that children received the vaccine according to Nigerian’s routine immunization schedule,” he said.
He said that the country had made steady progress in the ongoing COVID-19 vaccination campaign, noting that over 66 million persons were vaccinated so far, bringing the reach to 68 per cent.
“ Although there is progress, there are still pockets of rejections and misconceptions about the vaccines.
“This only means that there are persons out there who are aware of how vaccines work, hence there’s a need for us to strengthen our sensitisation to our communities, to ensure everyone is vaccinated,” he said.
According to him, the coming administration needs to invest heavily in the primary health care system as 60 per cent of all ailments according to real estimates, can be handled at the primary care level.
The Minister said a shift away from PHC was seen more to be the reason progress was not made due to a lack of enough attention and investment.
He further stressed the need to strengthen the country’s health system, while also urging the traditional leaders to recommit themselves to stopping the transmission of all forms of viruses, especially polio, which had been a major concern.
Alhaji Muhammad Sa’ad Abubakar, the Sultan of Sokoto, said the NTLC would continue to work closely with relevant stakeholders and the NPHCDA.
The Sultan, who was represented by Alhaji Haliru Ndansua Yahaya, the Emir of Shonga, said the review meetings were important to exchange ideas and also provide an avenue to learn more.
According to him, “We await the reports from the just concluded 39th Expert Review Committee (ERC) meeting on Polio Eradication and Routine Immunization in Nigeria (ERC).
He said that NTLC would work with its recommendations on routine immunisation intensification and Polio outbreak response in the country.
Meanwhile, the Chairman of NTLC and Emir of Argungu, Alhaji Samaila Mera, said the review meetings such as this were important to reflect on achievements and bottlenecks in the ongoing efforts to create demand for PHC services.
The objective of the meeting is to review the progress and the role played by traditional leaders in Primary Health Care Delivery at the grassroots.
Health
UNICEF emphasises importance of polio vaccination to caregivers


The United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) has encouraged caregivers in Katsina, Kano and Jigawa States to present their eligible children for the next round of polio vaccination exercise.
Mr Michael Banda, the Officer-in-charge of UNICEF Kano Field Office, made the call in Kano at a media dialogue on the polio campaign on Friday.
The media dialogue was organised by UNICEF in collaboration with the Kano State Primary Healthcare Development Agency, with participants from the above-mentioned states.
The News Agency of Nigeria (NAN) reports that the four-day polio vaccination exercise is scheduled to commence on April 20, across the three states.
According to the UNICEF Officer-in-charge of the Kano field office, the importance of the exercise cannot be overemphasised.
“As the data show, in Kano, Jigawa and Katsina, we have over 556,750 children who have not received one single dose of vaccination they should have received.
“These are referred to as zero-dose children. Such children inexorably are vulnerable to vaccine-preventable diseases, including poliomyelitis.
“This is unacceptable and must be tackled frontally. Not only is polio vaccination crucial, but all routine vaccinations are also critical to children’s survival.
“We must all work together to strengthen routine immunisation services and ensure that all children under five receive all vaccines, including the polio vaccine,” Banda said.
He added that, if all children got vaccinated and receive the vaccines they needed to receive, they would no longer be at risk of contracting polio, with attendant debilitating consequences.
He said that, rather they would have received the immunity which would protect them against vaccine-preventable diseases.
Banda emphasised that immunisation had been proven to be the most cost-effective protection against vaccine-preventable diseases.
“Let’s all work together, government, development partners, religious and traditional leaders, communities, NGOs, CSOs and the media, to ensure that every Nigerian child under five is vaccinated.
“This will protect them from not just polio, but all other vaccine-preventable diseases,” he appealed.
According to the UNICEF official, managing misinformation and vaccine hesitancy for Polio and overall vaccination is very crucial in Nigeria to stop the outbreak.
He stressed that the role of the media, including social media, was important in this aspect.
Health
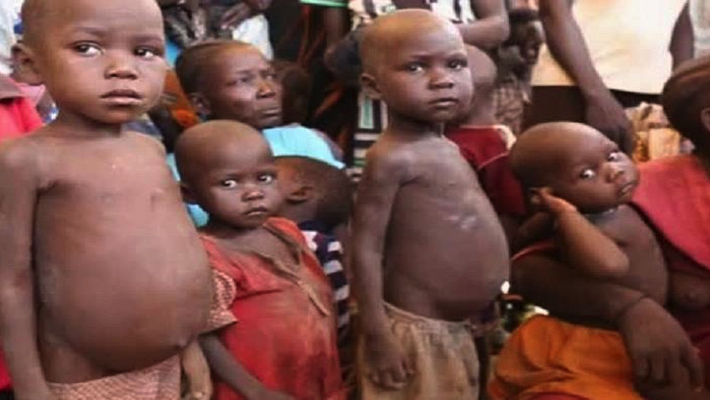
Over 1,800 malnourished kids recovered in six months in Bauchi — CSOs

Rauf Oyewole, Bauchi
The Coalition of Civil Society –Scaling Up Nutrition in Nigeria, Bauchi State Chapter has said that through its partnership with other implementing partners they have assisted over 1,800 malnourished children to recover from Severe Acute Malnutrition (SAM).
The Secretary of the Network, Dabis Mwalike while addressing journalists as part of the activities marking the 10th year anniversary of the network, said that it also engaged in preventive measures against malnutrition in the state.
According to her, during the implementation, 698 healthcare providers were trained across the 20 local government areas of Bauchi, 400 community-based volunteers were trained while 4,229 comprising 2,059 males and 2,170 females, children under five identified with SAM and 7,743 made of 3661males and 4082 females, children under five identified with Moderate Acute Malnutrition (MAM).
She added that 1,825 children under five identified with SAM and MAM recovered. While 202 PHCs established food banks.
She said that despite all the achievements, malnutrition remains a concern to public health and a threat to child survival, growth, and development in the country, and Bauchi State according to NNHS (2018) and NDHS (2018) the State stunting rate is 46 percent, wasting is 9.5 percent while underweight is 28.2 percent and overweight is 0.5 percent.
Health
Capacity training will reduce migration of health workers- NPHCDA


-
Finance3 months ago
Court orders Sen. Victor Umeh to repay N136m bank debt to AMCON
-



 Abuja Update2 months ago
Abuja Update2 months agoUNDP, FG partnership needed to achieve inclusion, equity- Minister
-
Abuja Update4 weeks ago
Banks drive stock market performance with N147bn gain
-



 Infotech3 weeks ago
Infotech3 weeks agoWorld Backup Day: NITDA urges Nigerians to ensure backup of data
-
capital market2 years ago
Rt.briscoe, FBNH, Others halts negative performance of stock market
-



 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoImmunisation: FG, GAVI seek synergy with Sokoto Govt.
-
Infotech1 week ago
Forex for Beginners: Unveiling the currency exchange and how to trade it
-
Submission Guidelines4 months ago
CALL FOR SUBMISSIONS: POETRY COLUMN-NND








