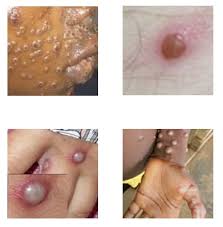
The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) has reported 39 confirmed cases of Mpox across 19 states and the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) in 2024, with no fatalities recorded.
The NCDC’s situation report for weeks 29 to 32, released on August 19, 2024, indicates that Mpox spreads through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated materials such as clothing and bedding.
Ogun State has the highest number of suspected cases at 141, followed by Lagos with 95 and Bayelsa with 87. Bayelsa leads in confirmed cases with five, while Enugu and Cross River each have four confirmed cases.
Suspected cases are distributed as follows: Kebbi 19, Ondo 18, Anambra 18, FCT 17, Benue 17, Rivers 10, Nasarawa 14, Plateau 11, Adamawa 11, Abia 10, Zamfara 7, Edo 6, Ebonyi 6, Taraba 5, Kano 5, Oyo 4, Gombe 4, Kogi 4, Jigawa 3, Kwara 3, Katsina 2, Bauchi 2, Sokoto 1, and Kaduna 1.
Compared to previous years, the 2024 data shows a marked decrease in both suspected and confirmed cases. In 2023, there were 1,182 suspected cases and 98 confirmed cases with two deaths and a 2.0% case fatality rate. In contrast, 2024 has seen 786 suspected cases with no fatalities.
The NCDC continues to monitor the situation, urging the public to be vigilant, maintain good hygiene, and avoid contact with infected individuals or contaminated materials.
The Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) recently declared the Mpox outbreak a Public Health Emergency of Continental Security (PHECS).
This decision was made due to 2,863 confirmed cases and 517 deaths reported across 13 African countries in 2024. This is the first such declaration by Africa CDC since its establishment in 2017. The agency emphasized the need for collective action, resource mobilization, and strategic responses to tackle the crisis.
Africa CDC Director General Dr. Jean Kaseya highlighted the importance of building partnerships and fortifying health systems, noting that there are currently no travel restrictions. Mpox outbreaks have now been reported in 13 African countries, including some previously unaffected nations such as Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, and Uganda.